CSRD. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) requires companies to report on the impact of corporate activities on the environment and society, and requires the audit (assurance) of reported information. EU Green Deal.SFDR is the first regulation set by the EU which aims to reorientate capital flow towards sustainable finance.The primary aim of the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) is to tackle greenwashing in the financial sector. As part of this mandate, the regulation requires fund managers to classify their funds based on their sustainability performance. The three classifications are Article 6, 8, and 9 funds.
Is CSRD part of EU taxonomy : Adherence to SFDR and CSRD aligns with EU Taxonomy requirements as the EU Taxonomy provides a classification system for sustainable economic activities that is applied within the CSRD and SFDR.
Is CSRD a standard or framework
CSRD establishes ESRS reporting framework
Each ESRS topical standard is organized to inform the reader on a uniform set of disclosure areas, including governance; strategy and business model; impact, risk and opportunity management; and metrics and targets.
What is CSRD in EU : Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive
On 5 January 2023, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) entered into force. It modernises and strengthens the rules concerning the social and environmental information that companies have to report.
Who does SFDR apply to Every financial market participant or financial advisor based in the EU must comply with SFDR reporting, across asset classes and including private equity. SFDR covers all EU investment management firms and advisors, including asset managers, banks, and insurers—along with all non-EU firms that target the EU market through the Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFM) Directive.
Does SFDR apply to all funds
Overall, the SFDR is applicable to two types of financial institutions: Financial advisers that provide investment or insurance advice concerning insurance-based investment products (IBIPs). Participants in the financial markets who produce and sell financial goods as well as provide portfolio management services.Overall, the SFDR and the CSRD are both part of a wider framework that aims to promote sustainable finance and sustainable economic activities in the European Union. Higher-quality disclosures across environmental areas will be an expectation from stakeholders – requiring standardized data akin to financial reporting.The CSRD extends the range of companies that must report on sustainability. It applies to: Large EU companies*; Most businesses with operations or securities in Europe, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (exemptions apply); While both frameworks have disclosure requirements, the CSRD includes additional requirements compared to the TCFD. In addition to climate-related disclosures, the CSRD mandates disclosure of actions taken to mitigate negative environmental and social impacts.
Who is exempt from SFDR : Who Needs To Follow The SFDR The SFDR's broad scope applies to all financial advisers (FAs) and financial market participants (FMPs) based in the EU. The SFDR defines FAs as entities that provide investment or insurance advice. FAs with fewer than three employees are not required to provide information.
Who has to report under CSRD : Who does the CSRD apply to The CSRD applies to large companies based in the EU or with an annual turnover of above €150 million in the EU.
Does SFDR apply to non EU companies
Who does the SFDR regulation apply to SFDR covers all EU investment management firms and advisors, including asset managers, banks, and insurers—along with all non-EU firms that target the EU market through the Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFM) Directive. The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) aims to improve the clarity and comparability of sustainability disclosures in financial market participants' investment policies and products.Overall, the CSRD builds upon and expands the principles set by the TCFD, incorporating a broader scope and a more holistic view of sustainability reporting.
Is SFDR mandatory : Every financial market participant or financial advisor based in the EU must comply with SFDR reporting, across asset classes and including private equity.
Antwort What is difference between CSRD and SFDR? Weitere Antworten – What does CSRD mean
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive
CSRD. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) requires companies to report on the impact of corporate activities on the environment and society, and requires the audit (assurance) of reported information. EU Green Deal.SFDR is the first regulation set by the EU which aims to reorientate capital flow towards sustainable finance.The primary aim of the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) is to tackle greenwashing in the financial sector. As part of this mandate, the regulation requires fund managers to classify their funds based on their sustainability performance. The three classifications are Article 6, 8, and 9 funds.

Is CSRD part of EU taxonomy : Adherence to SFDR and CSRD aligns with EU Taxonomy requirements as the EU Taxonomy provides a classification system for sustainable economic activities that is applied within the CSRD and SFDR.
Is CSRD a standard or framework
CSRD establishes ESRS reporting framework
Each ESRS topical standard is organized to inform the reader on a uniform set of disclosure areas, including governance; strategy and business model; impact, risk and opportunity management; and metrics and targets.
What is CSRD in EU : Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive
On 5 January 2023, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) entered into force. It modernises and strengthens the rules concerning the social and environmental information that companies have to report.
Who does SFDR apply to Every financial market participant or financial advisor based in the EU must comply with SFDR reporting, across asset classes and including private equity.
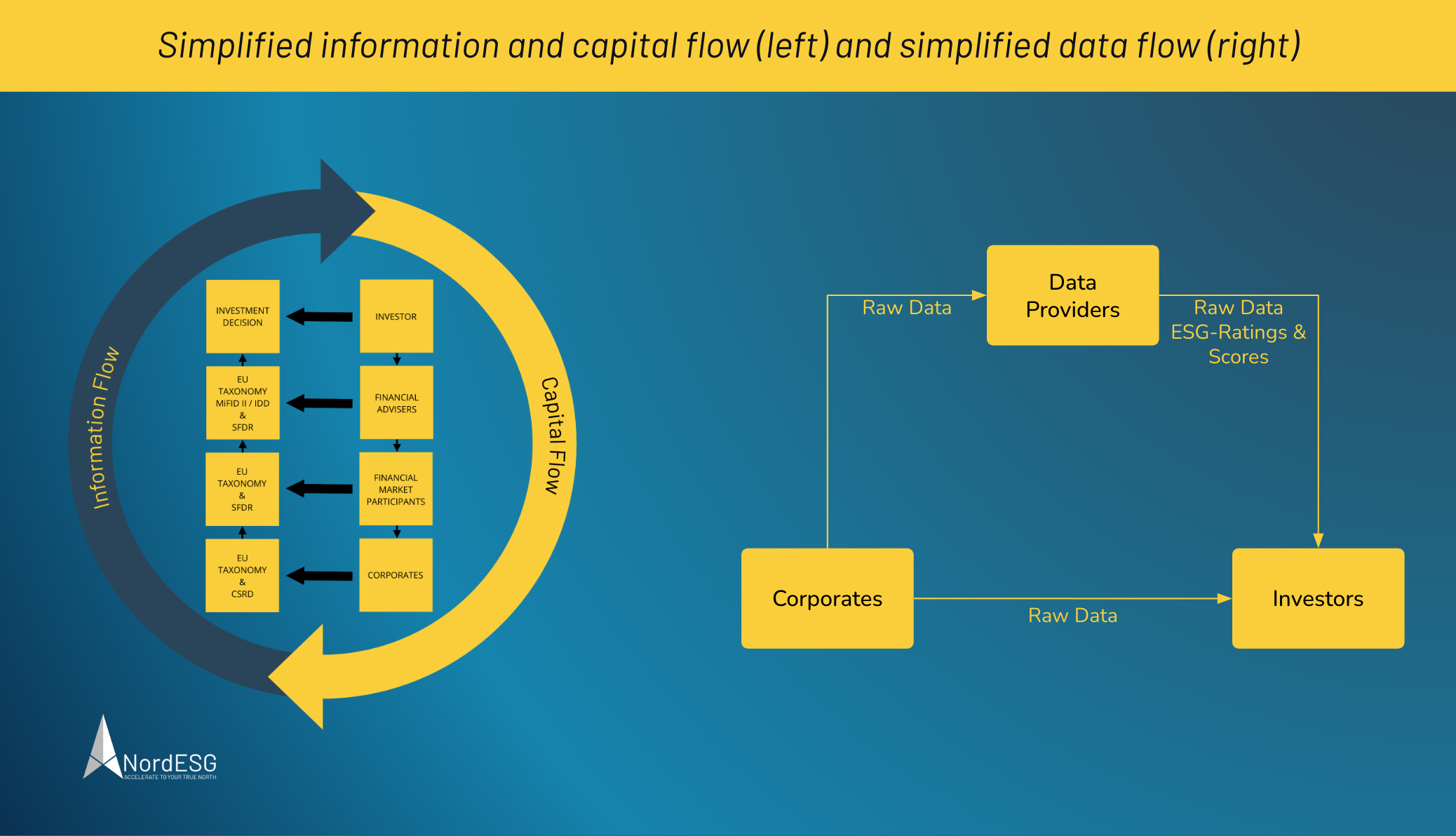
SFDR covers all EU investment management firms and advisors, including asset managers, banks, and insurers—along with all non-EU firms that target the EU market through the Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFM) Directive.
Does SFDR apply to all funds
Overall, the SFDR is applicable to two types of financial institutions: Financial advisers that provide investment or insurance advice concerning insurance-based investment products (IBIPs). Participants in the financial markets who produce and sell financial goods as well as provide portfolio management services.Overall, the SFDR and the CSRD are both part of a wider framework that aims to promote sustainable finance and sustainable economic activities in the European Union. Higher-quality disclosures across environmental areas will be an expectation from stakeholders – requiring standardized data akin to financial reporting.The CSRD extends the range of companies that must report on sustainability. It applies to: Large EU companies*; Most businesses with operations or securities in Europe, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (exemptions apply);

While both frameworks have disclosure requirements, the CSRD includes additional requirements compared to the TCFD. In addition to climate-related disclosures, the CSRD mandates disclosure of actions taken to mitigate negative environmental and social impacts.
Who is exempt from SFDR : Who Needs To Follow The SFDR The SFDR's broad scope applies to all financial advisers (FAs) and financial market participants (FMPs) based in the EU. The SFDR defines FAs as entities that provide investment or insurance advice. FAs with fewer than three employees are not required to provide information.
Who has to report under CSRD : Who does the CSRD apply to The CSRD applies to large companies based in the EU or with an annual turnover of above €150 million in the EU.
Does SFDR apply to non EU companies
Who does the SFDR regulation apply to SFDR covers all EU investment management firms and advisors, including asset managers, banks, and insurers—along with all non-EU firms that target the EU market through the Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFM) Directive.

The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) aims to improve the clarity and comparability of sustainability disclosures in financial market participants' investment policies and products.Overall, the CSRD builds upon and expands the principles set by the TCFD, incorporating a broader scope and a more holistic view of sustainability reporting.
Is SFDR mandatory : Every financial market participant or financial advisor based in the EU must comply with SFDR reporting, across asset classes and including private equity.